EER measures efficiency at hot outdoor conditions
Simple formula: Cooling output divided by power input
Higher EER means lower energy costs
| Rating | Meaning | Equipment | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EER | Energy Efficiency Ratio | Air Conditioners / Heat Pumps | Cooling | Energy Efficiency |
If you're joining us after reading our previous article about SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), then EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) will be much easier to understand, and if you haven't, we highly recommend reading it first to make understanding EER much easier.
Question: Since modern air conditioners use electrical energy to transfer heat from one area to another, have you ever wondered how much electrical energy it takes for your air conditioner to transfer a specific amount of heat when it's 95°F outside and 80°F inside your Houston home?
The Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) is an efficiency rating that expresses how much cooling capacity an air conditioner provides given a specific amount of electrical energy input. It's a simple energy input vs energy output efficiency rating that helps answer the question above.
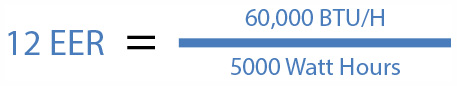
EER can tell us how many BTUs of cooling output an air conditioner will provide after using 5,000 Watt Hours of energy, or how much energy an air conditioner will consume when transferring 60,000 BTUs of heat.
EER is technically a ratio composed of the cooling output energy of an air conditioner measured in BTUs at specific indoor and outdoor conditions, divided by the air conditioner's electrical energy input measured in Watt Hours at those same conditions.

Using the example and formula above: If an air conditioner uses 5,000 Watt Hours of electrical energy to transfer 60,000 BTUs of heat energy out of a home, then its EER is 12:
Traditionally, EER labels were only found on smaller window units, but recent changes to energy efficiency laws have made EER take on an important role for central air conditioning systems as well.
In 2015, the DOE (Department of Energy) confirmed that HVAC efficiency standards would now vary by region, which included defining minimum EER requirements for warmer climates like the Southwest United States.
The Department of Energy (DOE) does not set mandatory minimum EER or EER2 ratings for residential air conditioners or heat pumps anywhere in the USA. The primary enforced metric is SEER2 (and HSPF2 for heat pumps), as these reflect seasonal efficiency and are deemed more representative of real-world energy use.
Some states or local jurisdictions (e.g., California) may reference EER for specific applications or commercial systems, but this is not the case for most jurisdictions.
Manufacturers must report EER2 as part of the DOE’s Appendix M1 testing procedures (effective January 1, 2023) for certification, but there are no minimum EER2 thresholds that must be met for compliance The EER2 is used to help homeowners make better choices and compare peak-load efficiency, which can be helpful in hot climates like Houston’s.
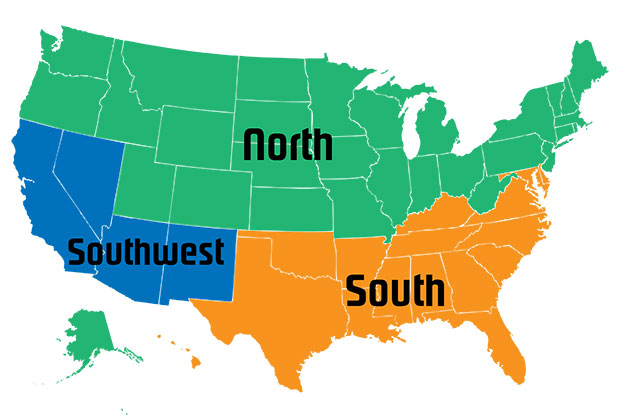
| Territory | Split A/C | Packaged A/C | Split Heat Pump | Packaged Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | 15 SEER | 15 SEER | 15 SEER 8.8 HSPF |
15 SEER 8.8 HSPF |
| South (including Texas) | 15 SEER | 15 SEER | 15 SEER 8.8 HSPF |
15 SEER 8.8 HSPF |
| Southwest |
15 SEER / 12.2 EER < 45,000 BTU/Hr 15 SEER / 11.7 EER ≥ 45,000 BTU/Hr |
15 SEER 11.7 EER |
15 SEER 8.2 HSPF |
15 SEER 8.8 HSPF |
80°F with 50% relative humidity
95°F with 39% relative humidity
When manufacturers have their equipment tested for EER and EER2 certification, they are tested at these conditions- These indoor and outdoor testing conditions are part of the DOE’s test procedures (often referenced in 10 CFR Part 430, Appendix M for SEER and EER, or Appendix M1 for SEER2/EER2) and simulate a high-load scenario, typical of hot climates like Houston.
Remember that SEER is calculated based on an indoor temperature of 80°F and an outdoor temperature of 82°F - only a 2-degree difference. This means SEER describes AC performance in mild climate conditions.
Because SEER is evaluated at mild temperature conditions that hot climates like Houston experience only a fraction of the time, SEER isn't as relevant to energy consumers in hot climates. It simply doesn't reflect real climate conditions and therefore doesn't reflect real energy consumption.
Just because an air conditioner has a high SEER rating does not mean it also has a high EER rating. Equipment that performs well in mild climates may not perform well in hot climates.
EER2 is the updated energy efficiency rating standard that replaces the original EER rating as of 2025. The "2" indicates the second generation of EER testing procedures.
So what has changed?
EER2 uses the same temperature conditions as EER, but with new updated testing procedures including a higher external static pressure test, which better reflect real-world fan operating conditions and ductwork scenarios. EER2 also takes in additional considerations like off-mode power consumption and more stringent requirements for variable-speed systems.
All-in-all due to these stricter testing conditions and updates to testing procedures, EER2 values are typically 4-5% lower than EER values for the same system- For example, a system with 15.0 EER might have a 14.3 EER2.
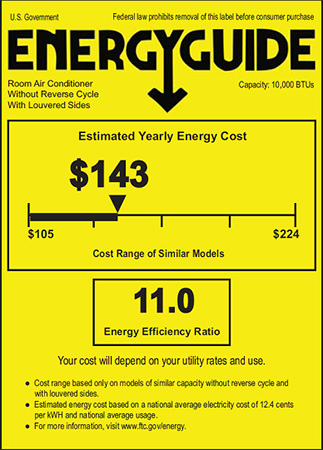
As of 2025, the FTC (Federal Trade Commission) requires EER information on the yellow EnergyGuide stickers found on HVAC equipment. The new labels include:
Shows which US regions the equipment can be installed in based on efficiency requirements.
The specific EER or EER2 rating is clearly displayed on the label.

For Houston's hot climate, we recommend choosing air conditioning systems with:
Look for EER2 ratings of 12+ for optimal performance during Houston's hottest days.
Higher EER2 ratings mean lower energy bills throughout Houston's long cooling season.
Our licensed HVAC professionals can help you select the most efficient system for your Houston home.